
‘Do you know the only thing that gives me pleasure? It’s to see my dividends coming in.’
To this day we can still relate to the words of American industrialist John D. Rockefeller, despite their utterance over a century ago. Be it a privately owned business or publicly listed stock, dividends come part and parcel with owning a portion of a business. Cash dividends have long been an effective tool used to attract investors to a company’s shares. ‘A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush’.
Dividends have historically been a way to disseminate information. A change in a company’s dividend could hint at financial health. In a world becoming increasingly dominated by information, mostly available at our fingertips, the power of the dividend, from this perspective at least, has diminished. Also, corporate finance departments have tools at their disposal, such as share buybacks, that have become increasingly popular.
Such phenomena, in addition to perhaps a shift in investor sentiment, have resulted in a reduction in the number of firms paying regular cash dividends to shareholders. The volume of dividends, however, has not necessarily decreased meaning that dividends are concentrated in a smaller number of companies. Dividend-targeting strategies, therefore, tend to be less diverse[1].
‘Do lower dividends mean lower returns?’
Not necessarily. Once a stock goes ex-dividend, it’s price decreases by the amount of the dividend, ceteris paribus. Not issuing a dividend would mean the cash remains in the company and thus is still part of the shareholder’s claim on assets.
Figure 1: Illustration of the impact of a dividend on stock price
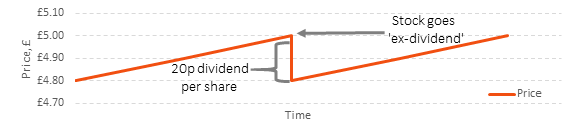
Source: Albion Strategic Consulting
‘Does it matter to me what my portfolio yields from dividends?’
Not really. We adopt what is called a ‘total return’ approach to investing[2]. We are agnostic to companies’ dividend policy and instead structure diversified portfolios with a focus on risk exposures. Your portfolio will usually generate some income from dividends each year, and sometimes some capital appreciation too. However, as figure 1 demonstrated, it doesn’t matter where that return comes from. One does not draw out cash, stare at two £20 notes and wonder: ‘which of these came from dividends and which from capital appreciation?’. Return, is return, is return.
Risk warnings
This article is distributed for educational purposes and should not be considered investment advice or an offer of any security for sale. This article contains the opinions of the author but not necessarily the Firm and does not represent a recommendation of any particular security, strategy, or investment product. Information contained herein has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable but is not guaranteed.
Past performance is not indicative of future results and no representation is made that the stated results will be replicated.
[1] Fatemi, A. & Bildik, R., (2012). “Yes, dividends are disappearing: Worldwide evidence,”
[2] For investors not requiring a ‘natural yield’ from the portfolio.




Recent Comments